Arctic Ocean overheating
Arctic Ocean Overheating: A Climate Change Crisis
The Arctic Ocean is experiencing alarming signs of overheating, raising concerns among scientists and environmentalists. This phenomenon, attributed to climate change, has significant implications for the delicate Arctic ecosystem and global climate patterns. Studies and research have shown that the Arctic region is warming at a faster rate compared to the rest of the planet.
Rising temperatures have led to the loss of sea ice, which acts as a reflective surface, bouncing back solar radiation into space. With less ice cover, more sunlight is absorbed by the dark ocean waters, causing further warming and creating a feedback loop. The consequences of the Arctic Ocean overheating are far-reaching.
The melting of sea ice affects wildlife habitats and disrupts the delicate balance of Arctic ecosystems. Species such as polar bears, walruses, and seals rely on ice for hunting, resting, and raising their young. As ice diminishes, their survival becomes increasingly challenging.
The warming of the Arctic Ocean also impacts global climate patterns. The Arctic plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate system, influencing ocean currents, weather patterns, and atmospheric circulation. Changes in the Arctic can have cascading effects, leading to altered weather conditions in other regions of the world.
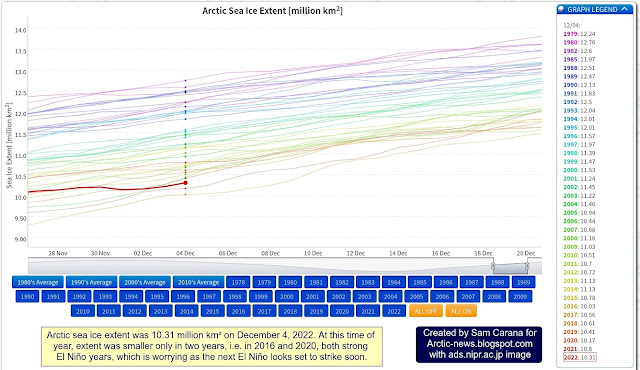
Arctic sea ice extent was 10.31 million km² on December 4, 2022. At this time of year, extent was smaller only in two years, i.e. in 2016 and 2020, both strong El Niño years. With the next El Niño, Arctic sea ice extent looks set to reach record lows.
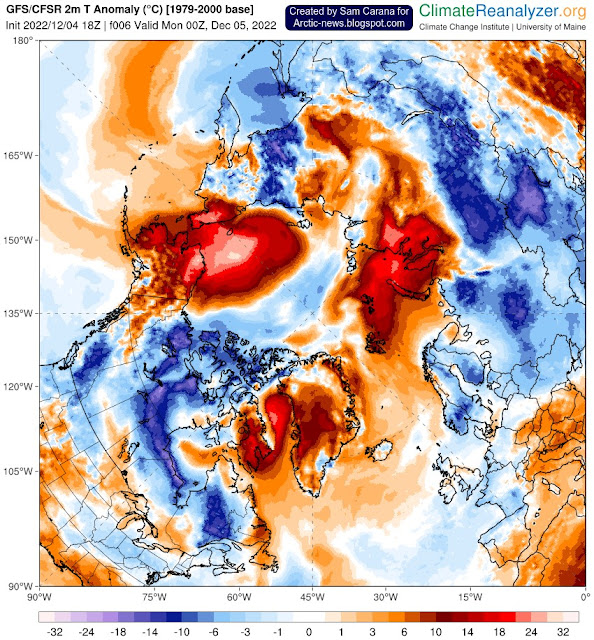
The image below shows high sea surface temperature anomalies near the Bering Strait on December 2, 2022, with a “hot blob” in the North Pacific Ocean where sea surface temperature anomalies are reaching as high as 7°C or 12.6°F from 1981-2011. The Jet Stream is stretched out vertically from pole to pole, enabling hot air to enter the Arctic from the Pacific Ocean and from the Atlantic Ocean.
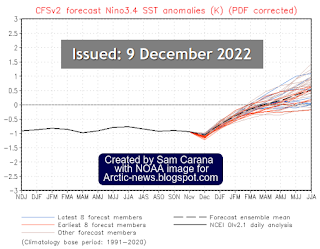
Given that we’re still in the depth of a persistent La Niña, these currently very high air temperature anomalies indicate that ocean temperatures are very high and that ocean heat is heating up the air over the Arctic.
This leaves only a very short time for Arctic sea ice to grow back in thickness before the melting season starts again, which means that there will be little or no latent heat buffer to consume heat when the melting season starts.
Furthermore, rising temperatures and changes to the Jet Stream contribute to formation of a freshwater lid at the sea surface at higher latitudes, resulting in further heating up of the Arctic Ocean.
As a result, more heat threatens to penetrate sediments at the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean that contain vast amounts of methane in hydrates and free gas, and result in abrupt release of huge amounts of methane, dramatically pushing up temperatures globally.
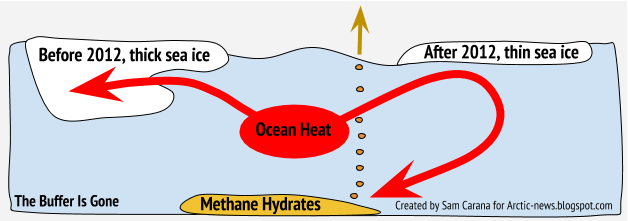 |
| [ The Buffer has gone, feedback #14 on the Feedbacks page ] |
The situation is dire and the right thing to do now is to help avoid or delay the worst from happening, through action as described in the Climate Plan.
Links
• Vishop sea ice extent
https://ads.nipr.ac.jp/vishop/#/extent
• NOAA ENSO: Recent Evolution,
Current Status and Predictions
• nullschool.net
• Climate Reanalyzer
• Naval Research Laboratory – HYCOM Consortium for Data-Assimilative Ocean Modeling
https://www7320.nrlssc.navy.mil/GLBhycomcice1-12/arctic.html
• Albedo, latent heat, insolation and more
• Cold freshwater lid on North Atlantic

Offered by our Wellcare World friend at
Trending Also -> Physiotherapy Terahertz Technology TeraMD
Wellcare World specializes in providing the latest advancements in wellness technology, supplementation, and lifestyle changes that improve health and increase the quality of people's lives. To learn more, visit WellcareWorld.com and begin living a better life today.
Share Us With Others