10 Best Posterior Chain Exercises for Stronger Lifts
Exercising is overall great for your body’s health. But if your workouts target specific areas of your body, it is highly possible that you will obtain the desired results in a short period of time. The same goes for posterior chain exercises.
Posterior chain exercises for stronger lifts are responsible for building and toning the muscles at the back of your body. Flexibility and coordination is also an advantage of these exercises. Lifting weights exert more pressure on your muscles. Don’t forget to add a healthy diet to your workout routine.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is a Posterior Chain?
- 2. What are Stronger Lifts?
- 3. 10 Best Posterior Chain Exercises For Stronger Lifts
- 3.1. Kettlebell Swing
- 3.2. Romanian Deadlift
- 3.3. Chin-Ups
- 3.4. Pendlay Row
- 3.5. Cobra
- 3.6. Cable Pull-Through
- 3.7. Hip Thrusts
- 3.8. Barbell on the Back
- 3.9. Barbell/Dumbbell Row
- 3.10. Kettlebell Deadlift
- 4. Importance of Posterior Chain Exercises
- 5. FAQs
- 5.1. Are Posterior Chain Exercises Great for Pelvic Mobility?
- 5.2. Does Muscle Mass Increase with Posterior Chain Exercises?
- 6. Conclusion
1. What is a Posterior Chain?
The muscles at the back of your spine and legs are called the posterior chain muscles. They extend down from your skull to your calf and glutes. These are the most important muscles in your body as they strengthen an athlete’s explosiveness.
These muscles make up the posterior chain including the erector spine muscles, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, and calf muscles. Posterior chain muscles are responsible for straight body posture and hip joint mobility.
2. What are Stronger Lifts?
The lifting of heavy weights with proper form and technique is involved in stronger lifts. It increases muscle mass as well as strengthens your body muscles.
The increase in weight must be gradual. Avoiding overtraining reduces the chances of injury. Consistent training and proper nutrition are a must.
3. 10 Best Posterior Chain Exercises For Stronger Lifts
It targets posterior chain muscles only but effects can be seen in your whole body. Even your mood becomes better after just a session of the following exercises.
3.1. Kettlebell Swing
Kettlebell swings are great for the posterior chain and cardiovascular fitness. This exercise targets the muscles of the posterior chain which includes the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back. It is also beneficial for your core muscles.
To perform kettlebell swings:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Hinge at your hips and grab the kettlebell with both hands.
- While keeping your arms straight, swing the kettlebell between your legs.
- Meanwhile your chest must be up with your back in a straight position.
- When you reach the other end of the swing, drive your hips in the forward direction and squeeze your glutes.
- Bring the kettlebell across your shoulder height with your arms in a straight position.
- Repeat the whole exercise for 6 minutes and rest for 1 minute between each rep.
| Number of Reps | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|
| 17 Reps on Each Side | 6 Minutes | 1 Minute |
Kettlebell swings are recommended for conditioning exercises. For stronger lifts, you must start with a lighter weight and then gradually increase the weight.
3.2. Romanian Deadlift
The Romanian Deadlift (RDL) is a posterior chain exercise designed especially for strengthening your hamstrings and glutes. It also aids in developing a great body posture.
To Perform the Romanian Deadlifts:
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart with the barbell in front of you on the ground.
- The barbell must be close enough that it touches your legs.
- Hinge forward at the hips while keeping your back straight and knees slightly bent.
- Grab the barbell and stand straight while squeezing your glutes.
- Pause in the standing position for a second and lower the barbell back to the ground.
The Romanian deadlift is different from the conventional deadlift as it concentrates on the eccentric or lowering phase of the lift. That is why it is recommended for building hamstring and glute strength. Keep your back straight and your core engaged to avoid injuries.
| Number of Reps | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|
| 8-15 Reps on Each Side | 5 Minutes | 60 Sec |
3.3. Chin-Ups
Chin-ups primarily target the upper back muscles. These are performed by hanging from a bar with your palms facing your body and pulling your body upward until your chin is above the bar.
To Perform Chin-Ups:
- Stand in front of a pull-up bar and hold the bar with your palms facing your body.
- The bar must be high enough that your feet must not touch the ground.
- Your hands must be slightly wider than the shoulder-width distance.
- Engage your back muscles and pull your body towards the bar until your chin is above the bar.
- Inhale when you go up the bar and exhale when you appear in the original position.
- Repeat the exercise for 5 to 6 minutes.
- Increase the reps of the exercise when you feel complacent with existing weight.
| Number of Reps | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|
| 12 Reps on Each Side | 4 Minutes | 60 Sec |
3.4. Pendlay Row
Pendlay row is a weightlifting exercise that targets the upper back muscles: latissimus dorsi, and trapezius. It was named after the weightlifting coach, Glenn Pendlay. It is a variation of the bent-over barbell row. When compared with the bent-over barbell, pendlay row allows you to reset your form and generate more power on each repetition. It allows your body to lift heavier weights and build more strength in your upper back muscles.
To perform pendlay row exercise:
- Stand in front of the barbell with your feet hip-width apart.
- Grab the barbell by bending your knees. Your grip on the barbell must be an overhand grip.
- Your back must be straight and your shoulders lifted.
- Pull the barbell towards your chest, keeping your elbows close to the body.
- After lifting the weight, you will feel a contraction in your chest.
- As the barbell reaches your chest, lower it back to the initial position.
| Number of Reps | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|
| 15-20 Reps on Each Side | 8 Minutes | 1 Min |
3.5. Cobra
Although there aren’t any weights involved in cobra, this exercise allows you to build flexibility.
To perform the cobra exercise:
- You must lay by facing down on the ground.
- Keep your arms by your side and rotate your hands in such a way that your thumbs are pointed towards the roof.
- Lift your chest off the ground and squeeze your glutes.
- Hold the position for at least 1 minute and repeat the exercise at least 5 times.
3.6. Cable Pull-Through
The cable-pull-through is an exercise that targets the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back muscles. It is performed using a cable machine, which provides resistance across a wide range.
To perform cable-pull through:
- Stand straight across the cable machine facing the opposite side.
- Keep your feet shoulder-width apart and straighten your back.
- Grab the rope handle with an overhand grip.
- Hinge at the hips and push your hips back as you lower yourself towards the ground.
- Keep your back flat and your head upward.
- Squeeze your glutes and push your hips forward as you stand back up to the starting point.
- Pull the rope handle up and forward as you rise.
| Number of Reps | Number of Sets | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-15 Reps on Each Side | 2-3 Sets | 5 Minutes | 2 Min |
3.7. Hip Thrusts
Hip thrusts are a lower body strength exercise. They are responsible for glute strength along with building endurance in the hamstrings.
To perform hip thrusts:
- Sit on the ground with your back against the bench or any elevated surface.
- Your feet must be flat on the ground, with bent knees and feet hip-width apart.
- Roll a barbell over your legs until it rests across your hip bones.
- Engage your glutes and lift your hips off the ground until your body is in a straight position. In short, lift the barbell with your hips.
- Lower your hips back to the initial position and keep your glutes and hamstrings tense.
- Inhale as you lift the barbell and exhale when you come down on the ground.
| Number of Reps | Number of Sets | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-8 Reps on Each Side | 3-5 Sets | 6 Minutes | 60 Sec |
3.8. Barbell on the Back
Barbell on the back is also called “Good Morning”. It is another form of Romanian deadlift. This exercise provides a much greater bend at the hips than the simple barbell squat. The difference between the two is that the barbell on the back builds more flexibility than the barbell squat. It is also good exercise for your hip flexors.
To perform barbell on the back:
- Lift the barbell on your upper back just below the base of your neck.
- Squat down bending at your hips and knee until your thighs are parallel to the ground.
- Squeeze your glutes and your hips must be protruding out, unlike the barbell squat.
- Arrive at the initial position and complete 3 sets of 6-8 reps for the exercise.
| Number of Reps | Number of Sets | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6-8 Reps on Each Side | 3 Sets | 10 Minutes | 2 Min |
3.9. Barbell/Dumbbell Row
Barbell/Dumbbell rows not only target your glutes and hamstrings but also target your upper body muscles. It can also be performed with a single arm. By performing the single-arm barbell row, the whole exercise intensifies and leaves a more long-lasting effect on your posterior chain muscles.
To perform barbell row:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Bend at your hips to grab the barbell with both hands.
- Your position must be that the inside of your elbow joint grazes your knee.
- Lift the barbell up and hinge your hips while putting pressure on your thighs and glutes.
- You can also lift the barbell to your chest and it will target the muscles of your back.
| Number of Reps | Number of Sets | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-20 Reps | 4 Sets | 15 Minutes | 2 Min |
To perform single-arm dumbbell row:
- Place your leg on a bench and secure position with your hand on the bench.
- Your upper body must be parallel to the floor.
- With your free hand, lift the dumbbell.
- Hold the weight and make sure that your lower back is straight.
- Breathe out and lift the weight to the side of your chest
- You will notice that your back muscles contract when you lift the weight.
- Breathe in as you go down.
- Repeat the movement with your other arm.
| Number of Reps | Number of Sets | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6-8 reps on each side | 3-4 sets with each arm | 10 minutes | 1 min |
3.10. Kettlebell Deadlift
Kettlebell deadlift is an exercise used to build body strength. Core stability is also one of the benefits of kettlebell deadlifts. In short, you lift the deadlift with your hips without putting much pressure on your back.
To perform kettlebell deadlifts:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Hinge at the hips while bending your knees slightly. Your back must be straight.
- Grab the kettlebell with your hands with an overhand grip.
- Your arms must be straight as you lift the kettlebell.
- Breathe in while lifting the kettlebell and breathe out as you go back to the initial position.
| Number of Reps | Number of Sets | Time | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-12 Reps | 3-4 Sets | 10 Minutes | 40 Sec |
4. Importance of Posterior Chain Exercises
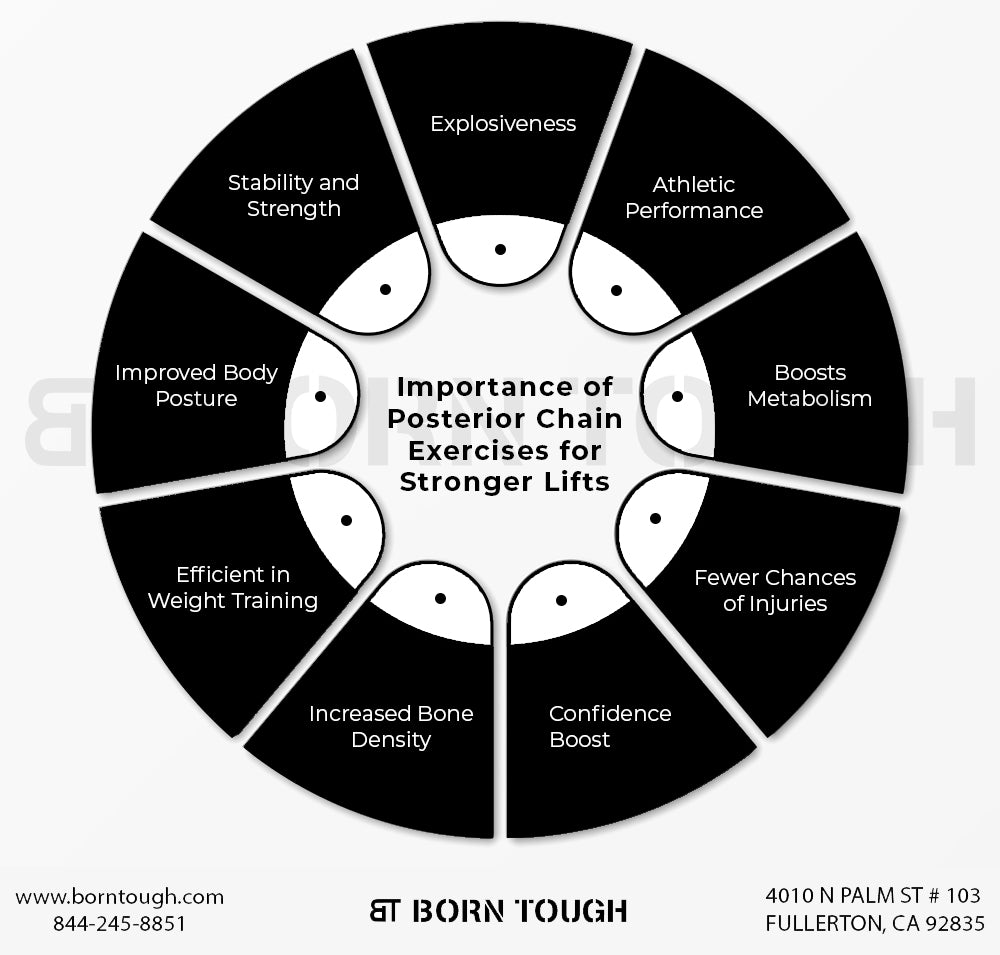
- Posterior chain exercises are great for building strength in your back muscles.
- The most visible change that you feel in your body is your fast pace. Even if you aren’t an athlete, your body will develop explosiveness.
- The above-mentioned exercises are specifically listed for you to develop stronger lifts.
- The muscles of the posterior chain are crucial for maintaining a great body posture. Strong glutes and hamstrings keep the spine in a perfect position that eventually leads to a great body posture.
- Working out displays immediate changes to your body. An increase in metabolic activity is the most obvious change after performing posterior chain exercises.
5. FAQs
5.1. Are Posterior Chain Exercises Great for Pelvic Mobility?
Pelvic Mobility is one of the core benefits of posterior chain exercises. The hip hinge joint develops great flexibility that makes movement easy for individuals.
5.2. Does Muscle Mass Increase with Posterior Chain Exercises?
Definitely, an increase in muscle mass is also an essential factor. More nutrients and supplements reach your muscles. Along with strengthening, your muscles also gain mass.
6. Conclusion
After reading this article, you are fully aware of how crucial posterior chain exercises are for your fitness. They not only shape your muscles but also develop strength and coordination. And do not forget to add a proper nutritious and healthy diet to your routine for fast results.
It is important to link other factors such as sleep and rest to your workout routine. It will leave an immensely positive effect on your body.
“This article is originally posted on borntough.com, and borntough.com own the sole copyright on this article. If you read this article outside borntough.com, please report this website to the authority because they have stolen the content from borntough.com and violated borntough copyright”

Offered by our Wellcare World friend at
Trending Also -> Physiotherapy Terahertz Technology TeraMD
Wellcare World specializes in providing the latest advancements in wellness technology, supplementation, and lifestyle changes that improve health and increase the quality of people's lives. To learn more, visit WellcareWorld.com and begin living a better life today.
Share Us With Others